AMC 8 – 1988 Problems (1988 AJHSME Problems)
Problem 1
The diagram shows part of a scale of a measuring device. The arrow indicates an approximate reading of
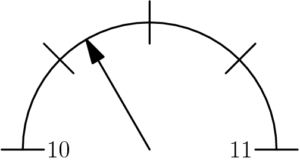
$\text{(A)}\ 10.05 \qquad$
$\text{(B)}\ 10.15 \qquad$
$\text{(C)}\ 10.25 \qquad$
$\text{(D)}\ 10.3 \qquad$
$\text{(E)}\ 10.6$
Problem 2
The product $8\times .25\times 2\times .125 =$
$\text{(A)}\ \frac18 \qquad$
$\text{(B)}\ \frac14 \qquad$
$\text{(C)}\ \frac12 \qquad$
$\text{(D)}\ 1 \qquad$
$\text{(E)}\ 2$
Problem 3
$\frac{1}{10}+\frac{2}{20}+\frac{3}{30} =$
$\text{(A)}\ .1 \qquad$
$\text{(B)}\ .123 \qquad$
$\text{(C)}\ .2 \qquad$
$\text{(D)}\ .3 \qquad$
$\text{(E)}\ .6$
Problem 4
The figure consists of alternating light and dark squares. The number of dark squares exceeds the number of light squares by
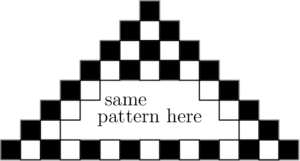
$\text{(A)}\ 7 \qquad$
$\text{(B)}\ 8 \qquad$
$\text{(C)}\ 9 \qquad$
$\text{(D)}\ 10 \qquad$
$\text{(E)}\ 11$
Problem 5
If $\angle \text{CBD}$ is a right angle, then this protractor indicates that the measure of $\angle \text{ABC}$ is approximately
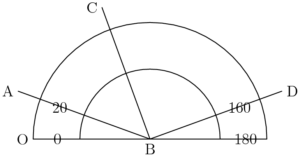
$\text{(A)}\ 20^\circ \qquad$
$\text{(B)}\ 40^\circ \qquad$
$\text{(C)}\ 50^\circ \qquad$
$\text{(D)}\ 70^\circ \qquad$
$ \text{(E)}\ 120^\circ$
Problem 6
$\frac{(.2)^3}{(.02)^2} =$
$\text{(A)}\ .2 \qquad$
$\text{(B)}\ 2 \qquad$
$\text{(C)}\ 10 \qquad$
$\text{(D)}\ 15 \qquad$
$ \text{(E)}\ 20$
Problem 7
$2.46\times 8.163\times (5.17+4.829)$ is closest to
$\text{(A)}\ 100 \qquad$
$\text{(B)}\ 200 \qquad$
$\text{(C)}\ 300 \qquad$
$\text{(D)}\ 400 \qquad$
$\text{(E)}\ 500$
Problem 8
Betty used a calculator to find the product $0.075 \times 2.56$. She forgot to enter the decimal points. The calculator showed $19200$. If Betty had entered the decimal points correctly, the answer would have been
$\text{(A)}\ .0192 \qquad$
$\text{(B)}\ .192 \qquad$
$\text{(C)}\ 1.92 \qquad$
$\text{(D)}\ 19.2 \qquad$
$\text{(E)}\ 192$
Problem 9
An isosceles triangle is a triangle with two sides of equal length. How many of the five triangles on the square grid below are isosceles?
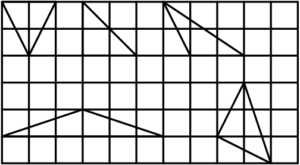
$\text{(A)}\ 1 \qquad$
$ \text{(B)}\ 2 \qquad$
$ \text{(C)}\ 3 \qquad$
$ \text{(D)}\ 4 \qquad$
$\text{(E)}\ 5$
Problem 10
Chris’s birthday is on a Thursday this year. What day of the week will it be $60$ days after her birthday?
$\text{(A)}\ \text{Monday} \qquad$
$\text{(B)}\ \text{Wednesday} \qquad$
$\text{(C)}\ \text{Thursday} \qquad$
$\text{(D)}\ \text{Friday} \qquad$
$\text{(E)}\ \text{Saturday}$
Problem 11
$\sqrt{164}$ is
$\text{(A)}\ 42 \qquad$
$\text{(B)}\ \text{less than }10 \qquad$
$\text{(C)}\ \text{between }10\text{ and }11 \qquad$
$\text{(D)}\ \text{between }11\text{ and }12 \qquad$
$\text{(E)}\ \text{between }12\text{ and }13$
Problem 12
Suppose the estimated $20$ billion dollar cost to send a person to the planet Mars is shared equally by the $250$ million people in the U.S. Then each person’s share is
$\text{(A)}\ 40\text{ dollars} \qquad$
$\text{(B)}\ 50\text{ dollars} \qquad$
$\text{(C)}\ 80\text{ dollars} \qquad$
$\text{(D)}\ 100\text{ dollars} \qquad$
$\text{(E)}\ 125\text{ dollars}$
Problem 13
If rose bushes are spaced about $1$ foot apart, approximately how many bushes are needed to surround a circular patio whose radius is $12$ feet?
$\text{(A)}\ 12 \qquad$
$\text{(B)}\ 38 \qquad$
$\text{(C)}\ 48 \qquad$
$\text{(D)}\ 75 \qquad$
$\text{(E)}\ 450$
Problem 14
$\diamondsuit$ and $\Delta$ are whole numbers and $\diamondsuit \times \Delta =36$. The largest possible value of $\diamondsuit + \Delta$ is
$\text{(A)}\ 12 \qquad$
$\text{(B)}\ 13 \qquad$
$\text{(C)}\ 15 \qquad$
$\text{(D)}\ 20\ \qquad$
$\text{(E)}\ 37$
Problem 15
The reciprocal of $\left( \frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{3}\right)$ is
$\text{(A)}\ \frac{1}{6} \qquad$
$\text{(B)}\ \frac{2}{5} \qquad$
$\text{(C)}\ \frac{6}{5} \qquad$
$\text{(D)}\ \frac{5}{2} \qquad$
$\text{(E)}\ 5$
Problem 16
Placing no more than one $\text{X}$ in each small square, what is the greatest number of $\text{X}$’s that can be put on the grid shown without getting three $\text{X}$’s in a row vertically, horizontally, or diagonally?
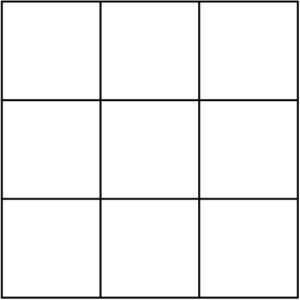
$\text{(A)}\ 2 \qquad$
$\text{(B)}\ 3 \qquad$
$\text{(C)}\ 4 \qquad$
$\text{(D)}\ 5 \qquad$
$\text{(E)}\ 6$
Problem 17
The shaded region formed by the two intersecting perpendicular rectangles, in square units, is
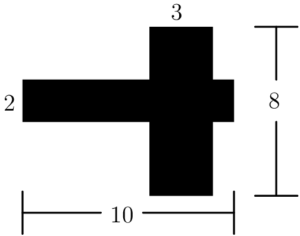
$\text{(A)}\ 23 \qquad$
$ \text{(B)}\ 38 \qquad$
$\text{(C)}\ 44 \qquad $
$\text{(D)}\ 46 \qquad $
$\text{(E)}\ \text{unable to be determined from the information given}$
Problem 18
The average weight of $6$ boys is $150$ pounds and the average weight of $4$ girls is $120$ pounds. The average weight of the $10$ children is
$\text{(A)}\ 135\text{ pounds} \qquad$
$ \text{(B)}\ 137\text{ pounds} \qquad$
$ \text{(C)}\ 138\text{ pounds} \qquad$
$ \text{(D)}\ 140\text{ pounds} \qquad$
$ \text{(E)}\ 141\text{ pounds}$
Problem 19
What is the $100\text{th}$ number in the arithmetic sequence: $1,5,9,13,17,21,25,…$?
$\text{(A)}\ 397 \qquad $
$\text{(B)}\ 399 \qquad$
$ \text{(C)}\ 401 \qquad$
$ \text{(D)}\ 403 \qquad $
$\text{(E)}\ 405$
Problem 20
The glass gauge on a cylindrical coffee maker shows that there are $45$ cups left when the coffee maker is $36\%$ full. How many cups of coffee does it hold when it is full?
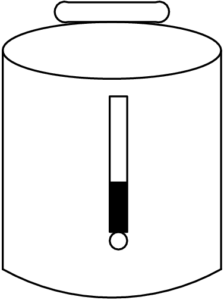
$\text{(A)}\ 80 \qquad$
$ \text{(B)}\ 100 \qquad$
$ \text{(C)}\ 125 \qquad $
$\text{(D)}\ 130 \qquad $
$\text{(E)}\ 262$
Problem 21
A fifth number, $n$, is added to the set $\{ 3,6,9,10 \}$ to make the mean of the set of five numbers equal to its median. The number of possible values of $n$ is
$\text{(A)}\ 1 \qquad$
$ \text{(B)}\ 2 \qquad$
$ \text{(C)}\ 3 \qquad$
$\text{(D)}\ 4 \qquad$
$ \text{(E)}\ \text{more than }4$
Problem 22
Tom’s Hat Shoppe increased all original prices by $25\%$. Now the shoppe is having a sale where all prices are $20\%$ off these increased prices. Which statement best describes the sale price of an item?
$\text{(A)}\ \text{The sale price is }5\% \text{ higher than the original price.}$
$\text{(B)}\ \text{The sale price is higher than the original price, but by less than }5\% .$
$\text{(C)}\ \text{The sale price is higher than the original price, but by more than }5\% .$
$\text{(D)}\ \text{The sale price is lower than the original price.}$
$\text{(E)}\ \text{The sale price is the same as the original price.}$
Problem 23
Maria buys computer disks at a price of $4$ for $<dollar>5$ and sells them at a price of $3$ for $<dollar>$$5$. How many computer disks must she sell in order to make a profit of $<dollar>100$?
$\text{(A)}\ 100 \qquad $
$\text{(B)}\ 120 \qquad$
$ \text{(C)}\ 200 \qquad$
$ \text{(D)}\ 240 \qquad$
$ \text{(E)}\ 1200$
Problem 24
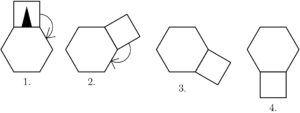
The square in the first diagram “rolls” clockwise around the fixed regular hexagon until it reaches the bottom. In which position will the solid triangle be in diagram $4$?
![]()
Problem 25
A palindrome is a whole number that reads the same forwards and backwards. If one neglects the colon, certain times displayed on a digital watch are palindromes. Three examples are: $\boxed{1:01}$, $\boxed{4:44}$, and $\boxed{12:21}$. How many times during a $12$-hour period will be palindromes?
$\text{(A)}\ 57 \qquad$
$\text{(B)}\ 60 \qquad$
$\text{(C)}\ 63 \qquad$
$\text{(D)}\ 90 \qquad$
$\text{(E)}\ 93$